Listen to our podcast 🎧
.jpeg)
Introduction
With modern enterprise networks expanding constantly across cloud and hybrid environments, the adoption of AI and Zero Trust has become a core part of internal security defence. Network security managers now rely on AI systems that detect and alert faster than traditional monitoring tools.
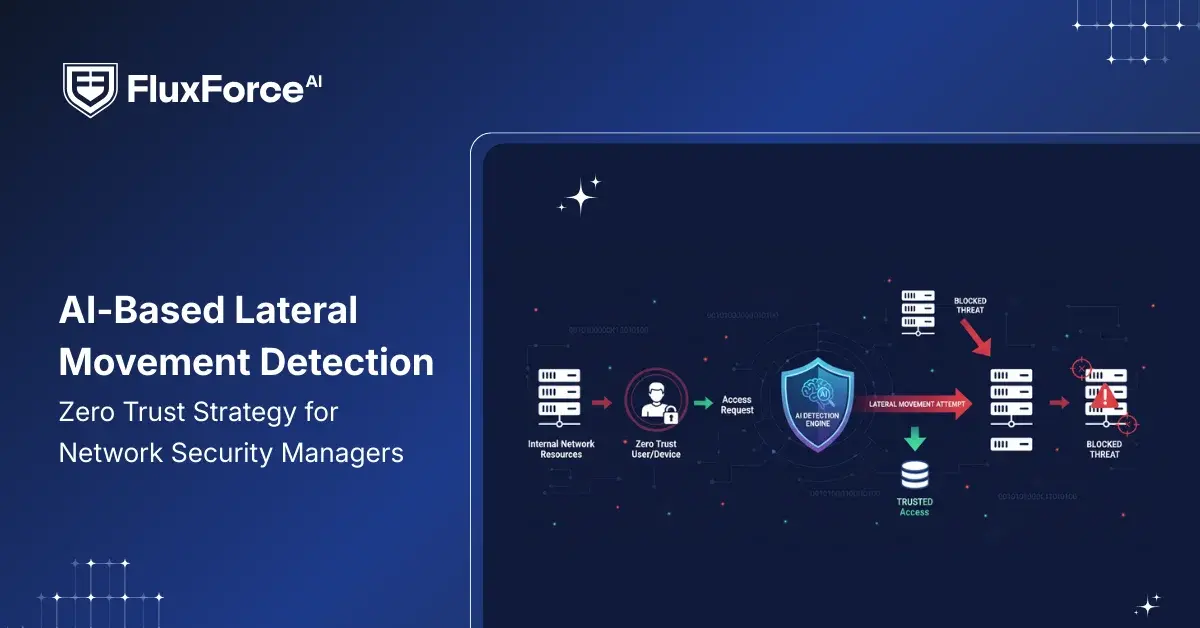
Across organizations, AI-based lateral movement detection helps stop attackers before they reach critical assets. When combined with Zero Trust, it removes implicit trust inside the network and restricts movement even after a breach.
Internal fraud and lateral-movement attacks in 2024 have caused significant financial and operational impact, highlighting the need for stronger internal controls. This article further explores how the strategic use of AI, combined with Zero Trust principles, improves visibility and prevents unauthorized activity within enterprise networks.
Attackers’ Advanced Lateral Movement Across Enterprise Networks
Attackers move quietly inside networks using compromised credentials and authorized paths that regular tools struggle to notice. They often follow predictable patterns that bypass perimeter monitoring and exploit gaps in identity controls.
Key patterns of lateral movement attackers use:
- Credential misuse: Attackers steal credentials and move as legitimate users to reach sensitive systems or cloud workloads.
- Privilege escalation: They slowly gain higher access rights by exploiting weak identity controls and role configurations.
- Unmonitored east–west traffic: Threats travel laterally within internal environments where monitoring is often limited.
- Shadow assets and unmanaged endpoints: Remote devices, legacy infrastructure, and shadow IT provide new hidden paths for attackers.
How AI Detects Lateral Movement in Enterprise Networks ?
Leveraging AI for internal attack path detection improves network security automation by monitoring user and device behaviour across the network. AI identifies compromised credentials and unusual activity before attackers can reach critical systems.

Core features of AI-based lateral movement detection:
1. Behavioural anomaly detection: AI builds a baseline of normal user and system activity. Deviations, such as accessing restricted files or unusual login patterns, trigger alerts for early threat detection.
2. Detecting compromised credentials with machine learning: Machine learning models track login times, device types, and locations. AI flags accounts with abnormal activity, prompting re-authentication or temporary access restriction.
3. Privilege escalation monitoring: AI monitors administrative changes and unusual privilege requests. Alerts are generated when an escalation is inconsistent with normal role behaviour.
4. Real-time intrusion detection: AI continuously evaluates logs and network events, identifying internal threats in real time and reducing dwell time.
5. East–west traffic analysis: AI monitors internal network flows to detect suspicious lateral connections, highlighting movement that might go unnoticed by traditional security tools.
6. Network security automation: AI systems can automatically respond to detected threats, limiting exposure and enforcing policies without waiting for manual intervention.

Integrating Zero Trust Cybersecurity Framework for Enterprise Defense
Key features include:
1. Identity-Based Access Control
Zero Trust enforces strict verification for every user and device. AI monitors access patterns in real time and identifies unusual behaviour, such as logins from unexpected locations or devices. When combined with automated policy enforcement, this ensures that only authorized users can reach critical applications or data, significantly reducing internal breaches caused by compromised credentials.
2. Strategic Network Segmentation
Networks are divided into isolated zones based on criticality and risk. AI continuously monitors east–west traffic between segments, identifying irregular or unauthorized flows. This approach limits the spread of attackers within the network. Enterprises report that segmentation combined with AI detection effectively contains breaches to a single zone, preventing attackers from moving laterally to other critical systems.
3. Continuous Verification
Access decisions are not based on a single login. AI continuously tracks device health, session activity, and behaviours across the network. Any deviation triggers additional authentication or temporary access suspension. This continuous verification prevents persistent internal threats and ensures that compromised accounts cannot maintain access unnoticed.
4. Policy-Driven Control
AI generates insights from user activity and risk patterns, which dynamically adjust Zero Trust policies. Automated enforcement ensures that high-risk actions, such as privilege escalation or unusual data access, are immediately blocked. Organizations implementing this capability have observed faster detection of internal threats and reduced dwell time, improving overall network security posture.
Enhancements of AI-Powered Zero Trust Network Security
AI-powered zero trust architecture combines automated threat detection with strict policy enforcement, giving network security managers a unified approach to internal protection.
How AI and Zero Trust work together to prevent lateral movement:

Real-World Deployment Insights: AI and Zero Trust in Action
Leading global companies have strengthened defence operations using Zero Trust network security combined with AI-powered lateral movement detection.
1. Microsoft
Microsoft applies Zero Trust across Azure and hybrid environments. AI models analyse user behaviour and internal activity to detect lateral movement and compromised credentials, enhancing network security automation.
2. Google
Google’s BeyondCorp model enforces identity-based access and micro-segmentation, while AI monitors user activity and internal network flows to prevent unauthorized lateral movement.
Aligning AI and Zero Trust: Best Practices for Network Security Managers
Strategic alignment of AI detection with Zero Trust policies ensures robust internal protection across modern enterprise networks. Applying these practices strengthens internal visibility, limits lateral movement, and helps security teams respond faster to evolving threats.
1. Adaptive access controls
AI-driven risk assessments should influence access policies automatically. This allows dynamic changes based on user behaviour or threat intelligence, minimizing windows where attackers could exploit trust assumptions within the network.
2. Strong identity governance
Regularly review user accounts, roles, and privileges. AI can flag inactive, orphaned, or high-risk accounts. Combining these insights with Zero Trust policies ensures users have only the necessary access for their responsibilities.
3. Inventory and segmentation
Maintain a complete inventory of servers, endpoints, cloud workloads, and IoT devices. Segment networks based on criticality. AI analytics can monitor communication between segments to detect unusual or unauthorized east–west traffic.
4. Continuous monitoring
AI tools continuously track logs, network traffic, and user behaviour across all zones. Suspicious activity, such as multiple logins from new locations or devices, triggers alerts, enabling faster identification of internal threats.
5. SOC collaboration with automation
SOC teams should integrate AI alerts into automated response workflows. For example, abnormal account behaviour can trigger a temporary access suspension. This reduces manual intervention and ensures consistent enforcement of Zero Trust policies.
6. Stepwise implementation
Implement Zero Trust gradually. Begin with high-value systems, establish baselines of normal user behaviour, integrate AI with identity and access management, and expand policies incrementally. This approach ensures practical adoption without operational disruption.

Conclusion
Using AI to detect internal threats and Zero Trust to enforce policies creates a robust, adaptive security posture for modern enterprises. AI enhances visibility, spotting lateral movement, compromised credentials, and anomalous behaviour across networks. Zero Trust ensures every access request is continuously verified, limiting unauthorized activity.
In distributed environments with extensive east–west traffic, AI audit trails provide deep behavioural insights for real-time detection of privilege escalation and lateral movement. Combined with Zero Trust, organizations shift from reactive investigation to proactive threat management, reducing dwell time and improving SOC efficiency. Together, they safeguard critical assets across cloud, hybrid, and on-premises networks.





Share this article