Listen to our podcast 🎧
.jpeg)
Introduction
In the insurance world, especially in insurance underwriting risk and claims management, everything runs on trust. But the same trust is what hackers and fraudsters often exploit. Breaches, insider threats, and stolen credentials are no longer rare infact they can happen to any company at any time.
Imagine you’re a claims director reviewing a high-value case, or an underwriting insurance company manager assessing a complex cyber insurance underwriting policy. On paper, everything looks fine, the numbers add up, and the documents are correct. Yet one wrong click by an employee, one stolen credential, or one unnoticed insider can undo months of work, drain millions of dollars, and break client trust.
Insurance is now one of the top three targets for cyberattacks worldwide. According to IBM, the average breach in the financial sector costs more than $6 million. This is where Zero Trust Security Architecture, smart identity access solutions, and identity management for insurance come into play. The idea is simple: “never trust, always verify.”
Every login, every access request, every file share is treated as a potential threat. This approach lowers the chances of unauthorized access, insider fraud, and underwriting leakage. For a cyber insurance underwriter, it’s even more important. How an insurer protects its own systems directly affects how it prices and sells cyber insurance policies. Strong internal security improves cyber insurance meaning and builds client confidence.
How Zero Trust Reshapes Underwriting and Claims Operations

Think about this: someone slips past your front desk and enters your office. Would you let them roam freely through file rooms, meeting halls, or executive cabins? Of course not. Yet, traditional insurance management solution systems often work like that. Once you’re “inside,” you are trusted.
Zero Trust works differently. It assumes no one is automatically trustworthy—whether it’s an employee, vendor, or even the CEO. Every request to access a policy file, claim report, or payout approval must be verified. Every. Single. Time.
What This Looks Like in Underwriting & Claims
- For Underwriting Managers: Risk files, client financial data, and fraud-check reports are protected by multiple verification layers. Ghost policies or fabricated claims become harder to sneak through. This strengthens underwriting cyber insurance processes.
- For Claims Directors: Identity & access management solution ensures payout systems, sensitive health records, and customer bank details aren’t open to everyone. Employees only access data they need, reducing exposure and improving insurance cybersecurity.
- For IT & Compliance Teams: Zero Trust allows real-time monitoring of suspicious activity. This way, unusual actions can be flagged before they cause data loss insurance claims or damage to reputation.
Companies adopting Zero Trust report nearly 50% fewer security incidents compared to older trust models.
Strategies for Implementing Zero Trust in Insurance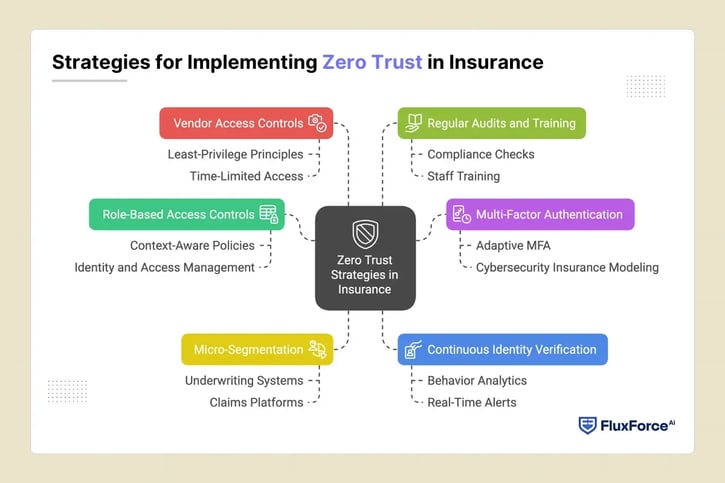
Underwriters and claims directors handle very sensitive data daily. Applying Zero Trust across workflows is critical to prevent mistakes and fraud.
- Role-Based Access Controls (RBAC) with Context-Aware Policies
Claims directors should make sure that underwriters and claims staff can only access the information they truly need for their job. For example, a junior claims analyst might be allowed to read customer documents, check policy details, or review claims history, but they should not be able to approve any payments or make changes to policies. RBAC help enforce these limits by defining exactly who can view, edit, or approve different types of data. Context-aware policies add another layer of protection by considering factors like the employee’s location, the device they are using, and the access time, flagging any unusual activity for review. Following guidance from experienced identity and access management consultants ensures that sensitive insurance underwriting risk files, claim records, and client data are properly protected while letting staff work efficiently within their authorized boundaries.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) Across All Access Points
Passwords alone are no longer enough to protect sensitive insurance data. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) should be required for every login, whether it’s underwriters reviewing fraud reports, claims staff processing payouts, or auditors accessing policy files. Adaptive Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) puts an extra layer of security by triggering additional verification steps for higher-risk activities, such as approving underwriting risk insurance policies, updating sensitive client information, or making changes to coverage limits. This makes sure that only the authorized users can perform critical actions, that reduces the chance of errors, fraud, or insider threats. Implementing MFA also supports cybersecurity insurance modeling and pricing because insurers can demonstrate strong internal security controls, which helps in accurately assessing risk and setting fair premiums.
- Micro-Segmentation of Insurance Data Systems
Instead of keeping all data together, micro-segmentation splits underwriting systems, claims platforms, and policyholder databases into smaller security zones. A breach in one area cannot automatically spread to others. For example, a compromised cyber insurer file won’t give access to customer health claims or payment details. This reduces risks and supports better insurance architecture practices.
- Continuous Identity Verification with Behavioral Monitoring
Zero Trust is about checking users continuously, not just once. Behavior analytics monitor underwriters’ and staff actions in real time. If a cyber underwriter downloads hundreds of files or accesses systems after hours, alerts are triggered immediately. This is important for cyber insurance risk assessment and keeping sensitive data secure.
- Strong Vendor and Third-Party Access Controls
Insurance companies often rely on external vendors—auditors, reinsurers, surveyors, and IT contractors. Claims directors should make sure third-party access follows least-privilege principles, is time-limited, and is constantly monitored. This prevents outsiders from creating gaps in underwriting cyber insurance or insurance cybersecurity systems.
- Regular Audits, Compliance Checks, and Training
Zero Trust isn’t just about technology. Regular identity access audits confirm that only authorized personnel access critical systems. Staff training helps underwriters and claims staff spot phishing emails or unusual requests before harm occurs. Following cyber insurance assessment standards keeps insurance and cyber security processes transparent and trustworthy.
-1.png?width=1200&height=628&name=hubspot%20blog%20(6)-1.png)
Shaping the Future of AI in Finance
Fluxforce research uncovers how banks and enterprises are adapting to fraud, compliance, and data challenges in 2025.
How Zero Trust Helps in Cyber Insurance and Claims Management
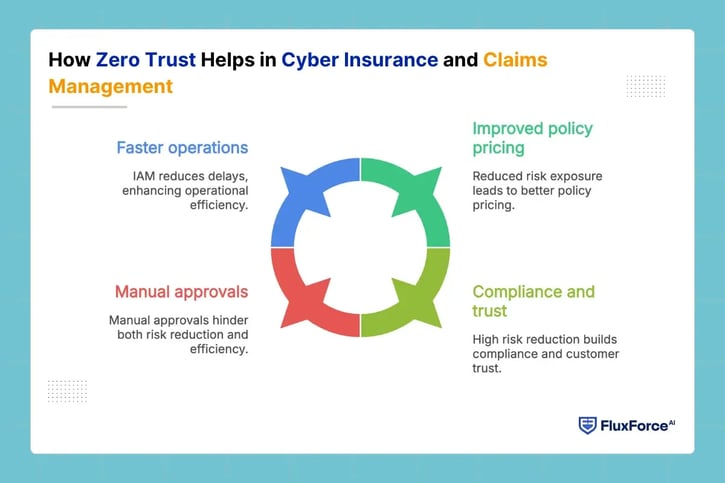
Zero Trust directly influences how insurance companies manage risks, set policy prices, and process claims. When cyber insurance underwriters review a company, they check how strong its IAM insurance practices are. Strong identity access management reduces chances of data leaks, insider fraud, and unauthorized approvals.
Key benefits include:
- Improved pricing for cyber insurance policies due to reduced risk exposure.
- Lower chances of data loss insurance events, helping compliance and customer trust.
- Faster operations as IAM reduces delays caused by manual approvals or password issues.
With Zero Trust, underwriting cyber insurance and claims processes become safer, faster, and more accurate.
Future of Zero Trust in Insurance: What Claims Directors Should Prepare For
The insurance sector is moving toward a model where identity access solutions are not just for compliance—they are competitive advantages. In the coming years, cyber insurance underwriting will rely on strong insurance architecture frameworks, and ongoing cyber insurance assessments.
Regulators are expected to enforce stricter data protection rules, making audits mandatory. Claims directors adopting Zero Trust early will adapt faster and better manage underwriting risk insurance.
New AI-driven tools, automated identity & access management solution, and real-time monitoring will help claims teams, underwriters, and network liability underwriting managers detect unusual activity before breaches happen.
Zero Trust blends security underwriting with smarter operations. Claims directors implementing it early will protect companies from costly breaches and build long-term client trust.
Conclusion
The insurance industry is changing fast. Rising fraud, stricter rules, and higher costs from data breaches mean stronger security is needed. Using Zero Trust in underwriting and claims helps directors protect their operations for the future.
Prebuilt AI modules, fraud detection systems, and identity management for insurance solutions make this shift faster, scalable, and regulation-ready. Cybersecurity insurance, combined with Zero Trust and IAM insurance practices, becomes a proactive defense.
In fact, cybersecurity insurance is an example of risk management strategy. By combining it with strong identity management for insurance and ongoing cyber insurance assessments, insurance companies protect assets and build stronger customer trust.


-1.png)
.webp)


Share this article